Research Projects
The biomechatronics lab is involved in a number of projects. You will find some information on both current and past projects in the pages below.
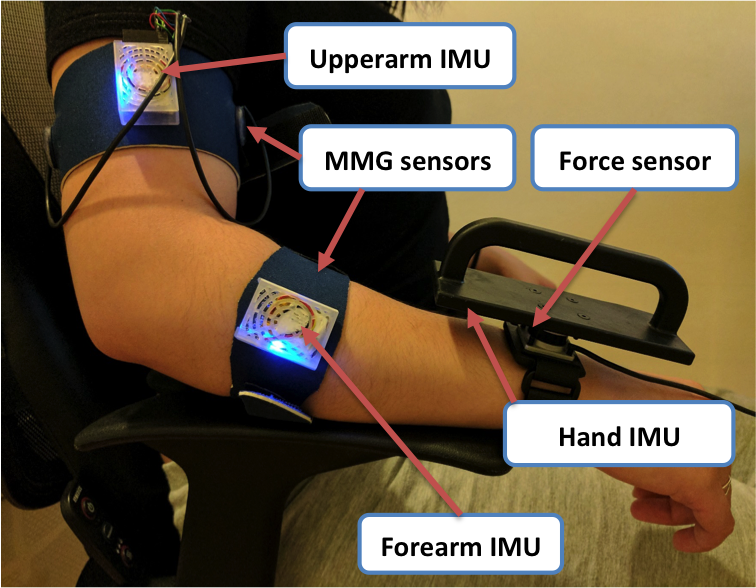
Muscle Sounds in Gesture Recognition
Samuel Wilson

Quantifying symptoms of Parkinson
Weiguang Ho/Paolo Angeles
Motion-based Grasp Selection
Marcus Gardner
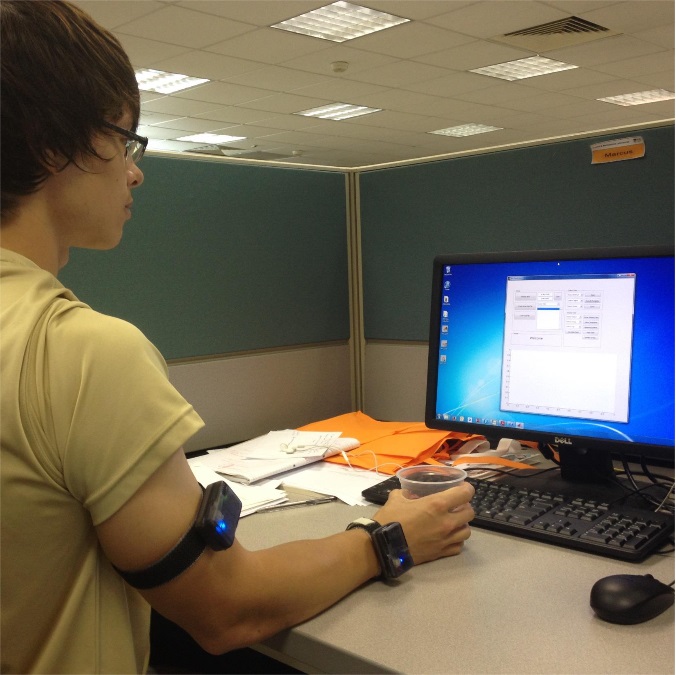

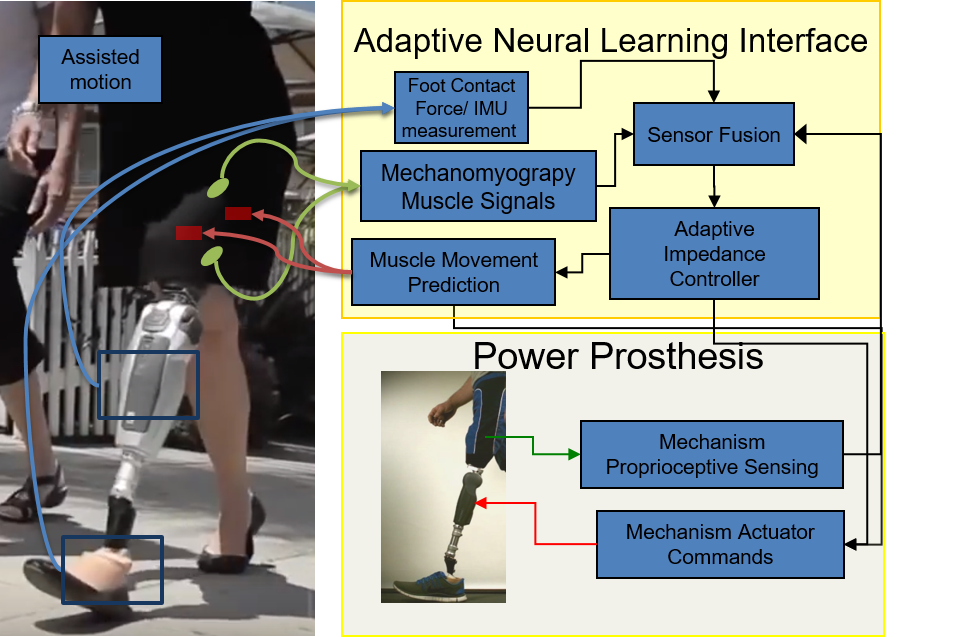
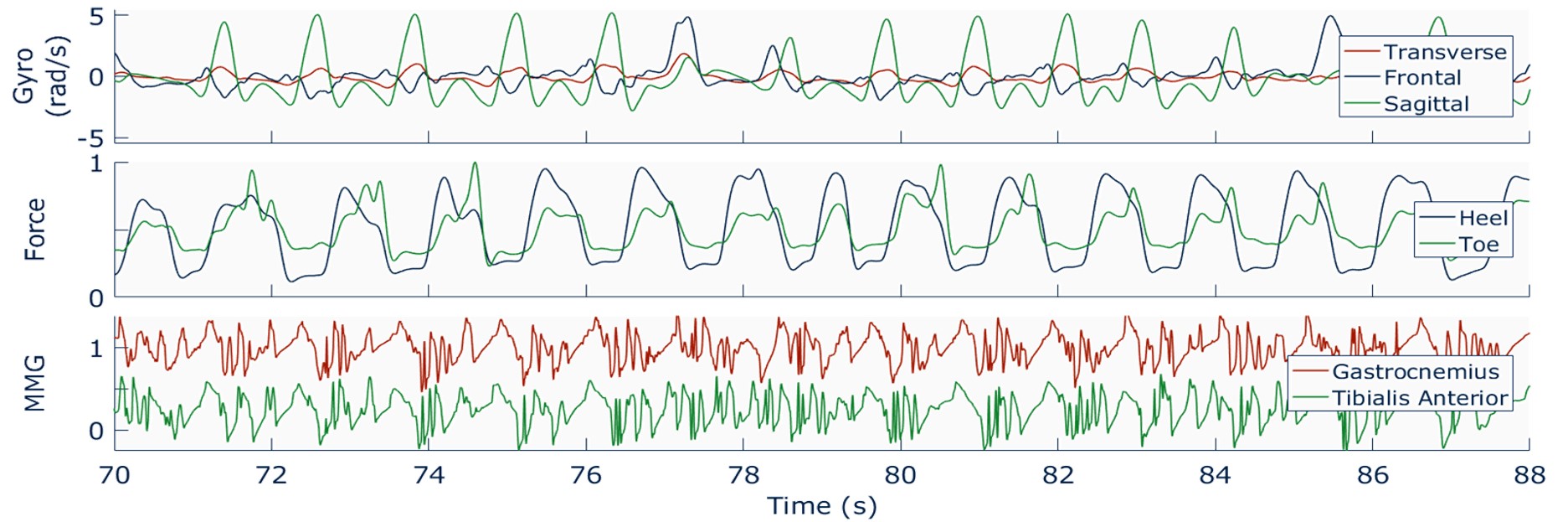
Sensory Motor Interface for Lower Extremity Robots ...
Filip P. Paszkiewicz, Samuel C. Wilson
Neurological Dysfunction in Balance: an Integrated ...
James Clarke
Unilateral Exoskeleton for Post-stroke Gait Rehabi ...
Christopher Caulcrick
Investigating novel forms of brain machine interfa ...
Thomas Martineau
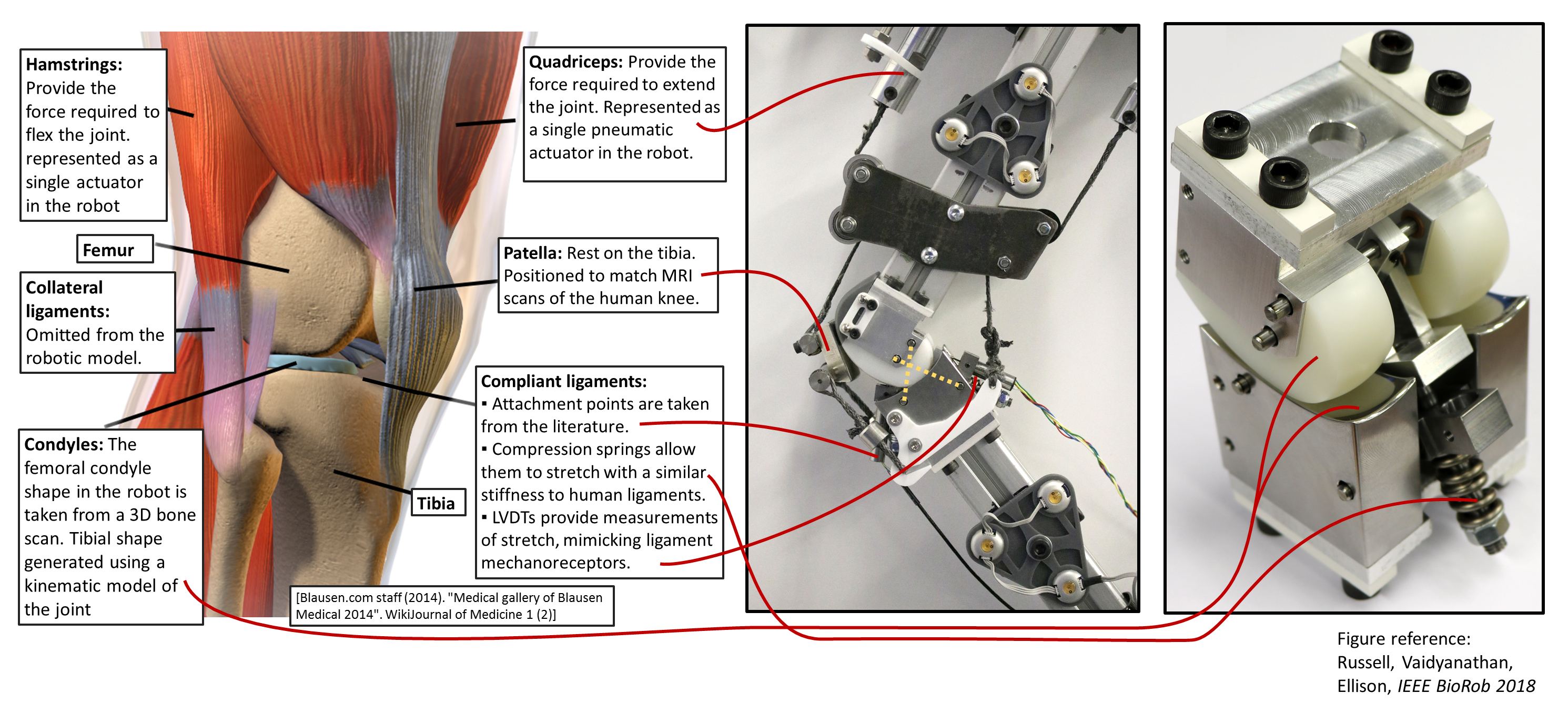
A Complete Robotic Knee As a Tool for a Better Und ...
Felix Russell
Stroke Lesion Symptom Mapping
Lewis Formstone
Morphing (Flying/Crawling) Robots
Richard Bachmann

Amphibious Robots
Alexander Boxerbaum/ Matthew Kline
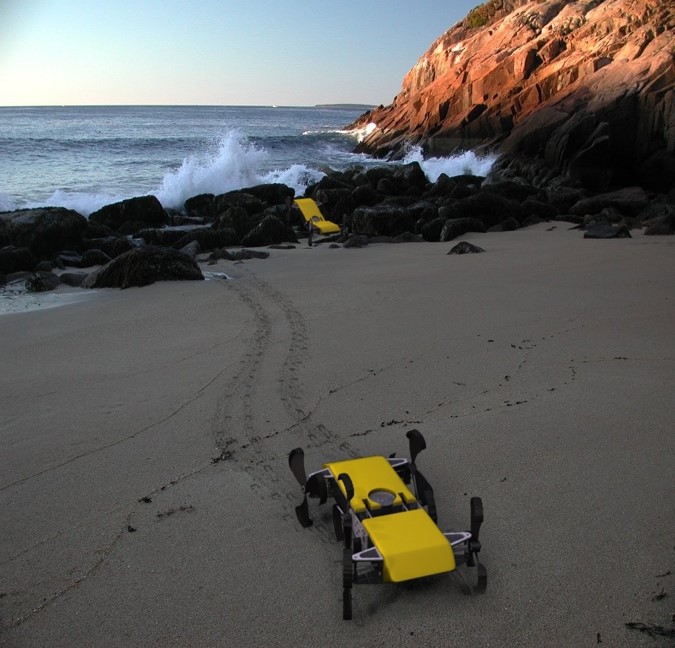

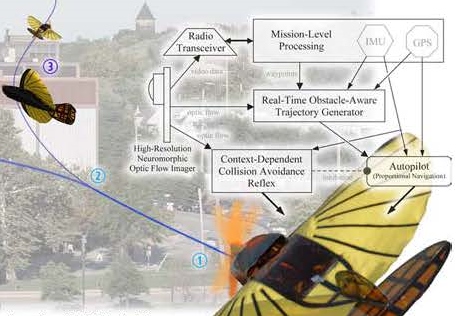
Insect Inspired Autonomy
Charles Williams
Rapidly Customizable Hand Exoskeleton
Thomas Burton/Thomas Martineau
Emotional Robotics
Ravi Vaidyanathan/Suresh Devasahayam
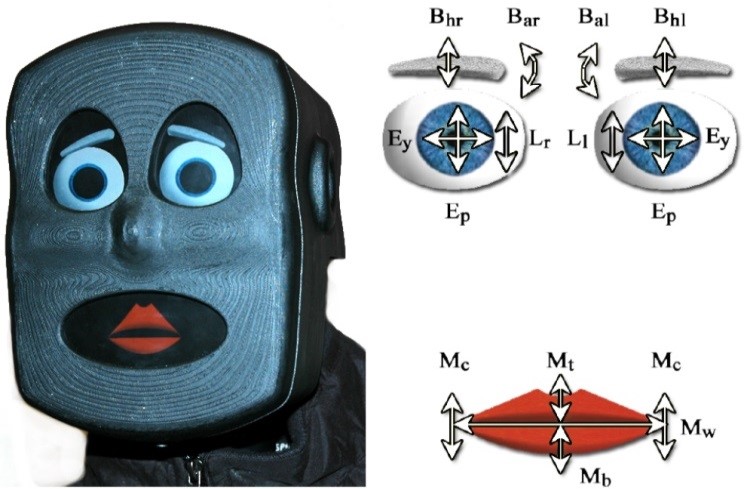
M-Mark Stroke Rehabilitation System
Alexander Wolff

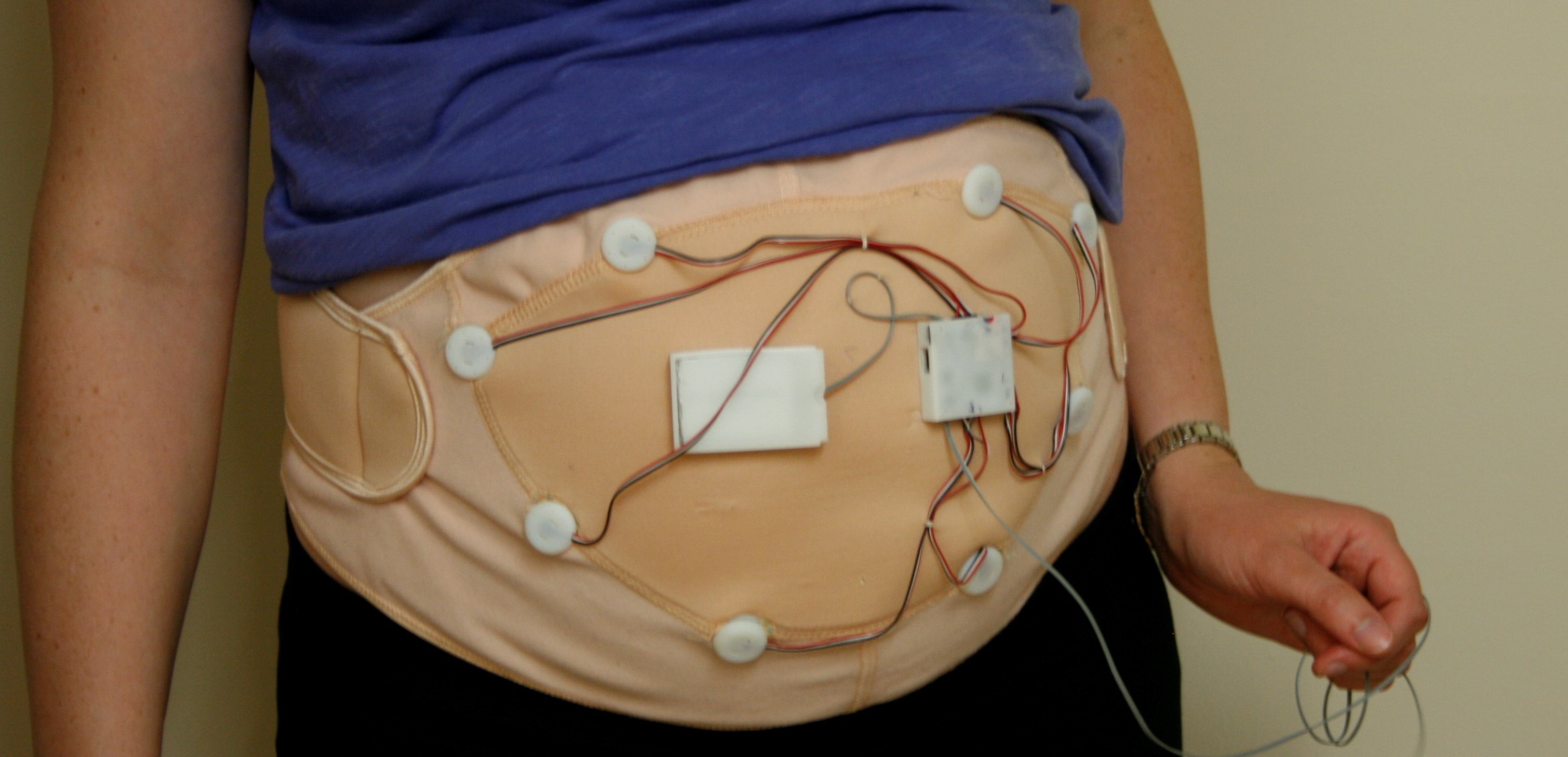
Wearable Fetal Movement Monitor
Abhishek Kumar Ghosh